








Mastering the Quirks of Irregular Plural Nouns
In the English language, nouns typically follow straightforward rules when forming plurals. You add an “s” to most nouns to indicate that there’s more than one of them. However, not all nouns conform to this rule. Some have irregular plural forms that require a different set of rules. In this article, we’ll dive into the world of irregular plural nouns, exploring what makes them unique, and how to use them correctly.
A list of some irregular plural nouns
100 examples of singular and plural / irregular nouns list:
Domino – Dominoes
Scarf – Scarfs – Scarves
Cactus – Cacti
Goose – Geese
Baby – Babies
Moose – Moose
Matrix – Matrixes – Matrices
Copy – Copies
Medium – Media
Ox – Oxen
Calf – Calves
Waltz – Waltzes
Axis – Axes
Volcano – Volcanoes
Man – Men
Synopsis – Synopses
Woman – Women
Child – Children
Mouse – Mice
Syllabus – Syllabi – Syllabuses
Tooth – Teeth
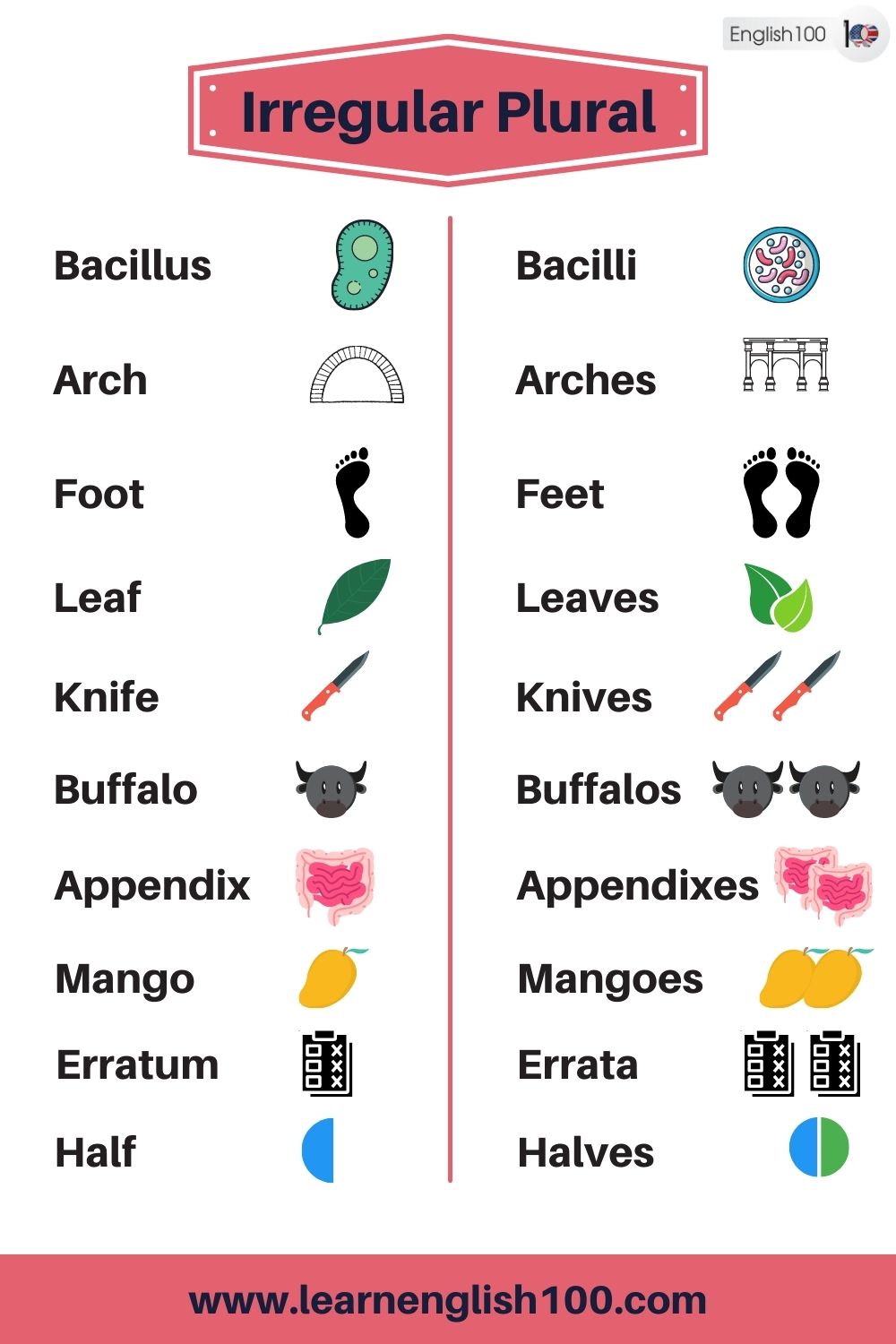
Bacillus – Bacilli
Arch – Arches
Foot – Feet
Leaf – Leaves
Knife – Knives
Buffalo – Buffalos – Buffaloes
Appendix – Appendices – Appendixes
Mango – Mangoes
Erratum – Errata
Half – Halves
Echo – Echoes
Octopus – Octopi
Hoof – Hooves – Hoofs
Stimulus – Stimuli
Thief – Thieves
Aircraft – Aircraft
Sheep – Sheep
Wolf – Wolves
Deer – Deer
Mosquito – Mosquitoes
Stratum – Strata
Dwarf – Dwarves – Dwarfs
Atlas – Atlases
Splash – Splashes
Person – People
Means – Means
Memorandum – Memoranda
Tomato – Tomatoes
Aquarium – Aquaria – Aquariums
Caveman – Cavemen
Policewoman – Policewomen
Tornado – Tornadoes
Son-in-law – Sons-in-law
Louse – Lice
Diagnosis – Diagnoses
Hoax – Hoaxes
Vertebra – Vertebrae
Elf – Elves
Zero – Zeros – Zeroes
Wife – Wives
Datum – Data
Abyss – Abysses
Millennium – Millenniums – Millennia
Larva – Larvae
Brush – Brushes
Fish – Fish
Shelf – Shelves
Cherry – Cherries
Iris – Irises
Series – Series
Apparatus – Apparatuses
Spices – Spices
Tax – Taxes
Mess – Messes
Hovercraft – Hovercraft
Tableau – Tableaux – Tableaus
Runner-up – Runners-up
Fly – Flies
Alga – Algae
Curriculum – Curricula
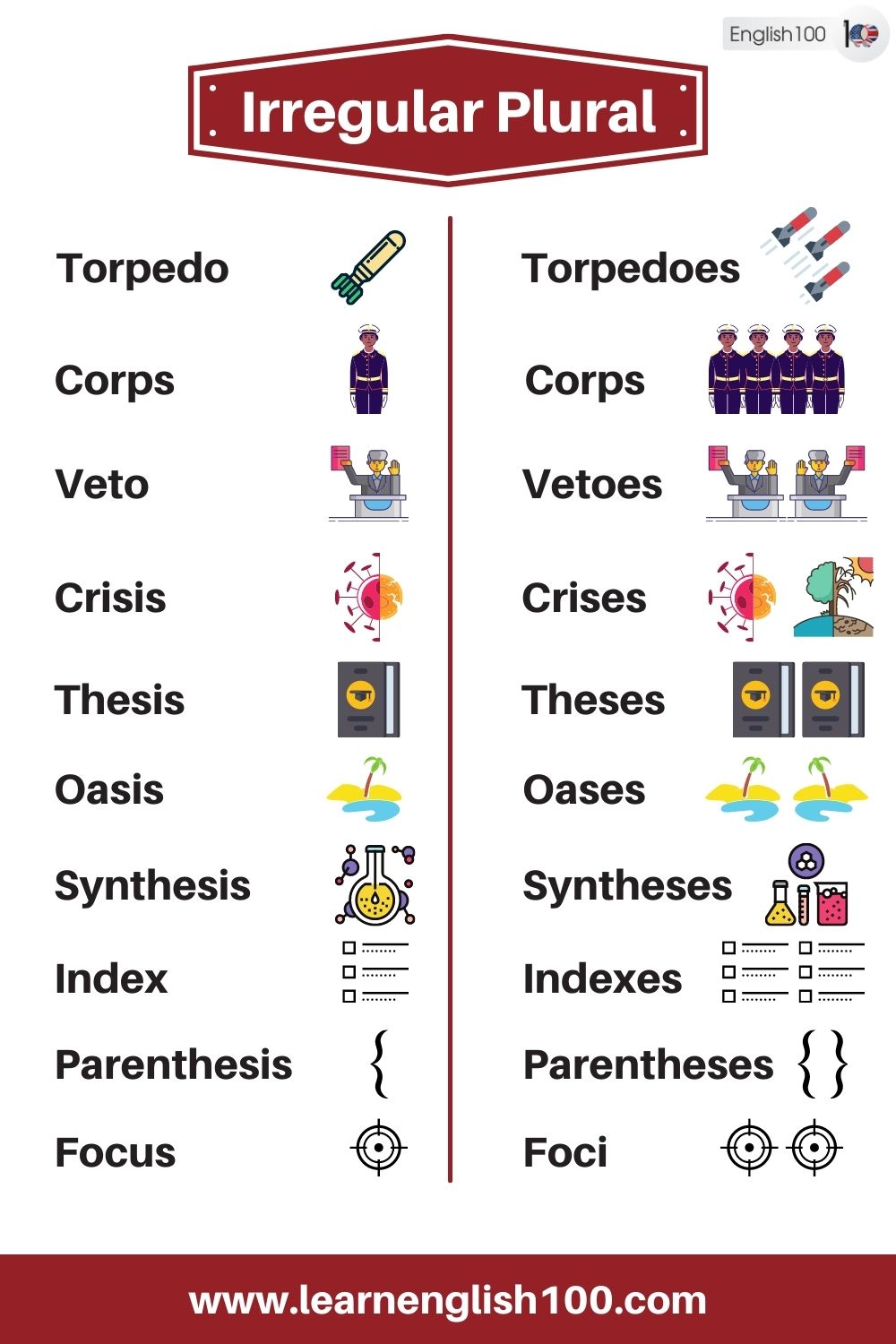
Torpedo – Torpedoes
Corps – Corps
Veto – Vetoes
Crisis – Crises
Thesis – Theses
Oasis – Oases
Synthesis – Syntheses
Index – Indices – Indexes
Parenthesis – Parentheses
Focus – Foci
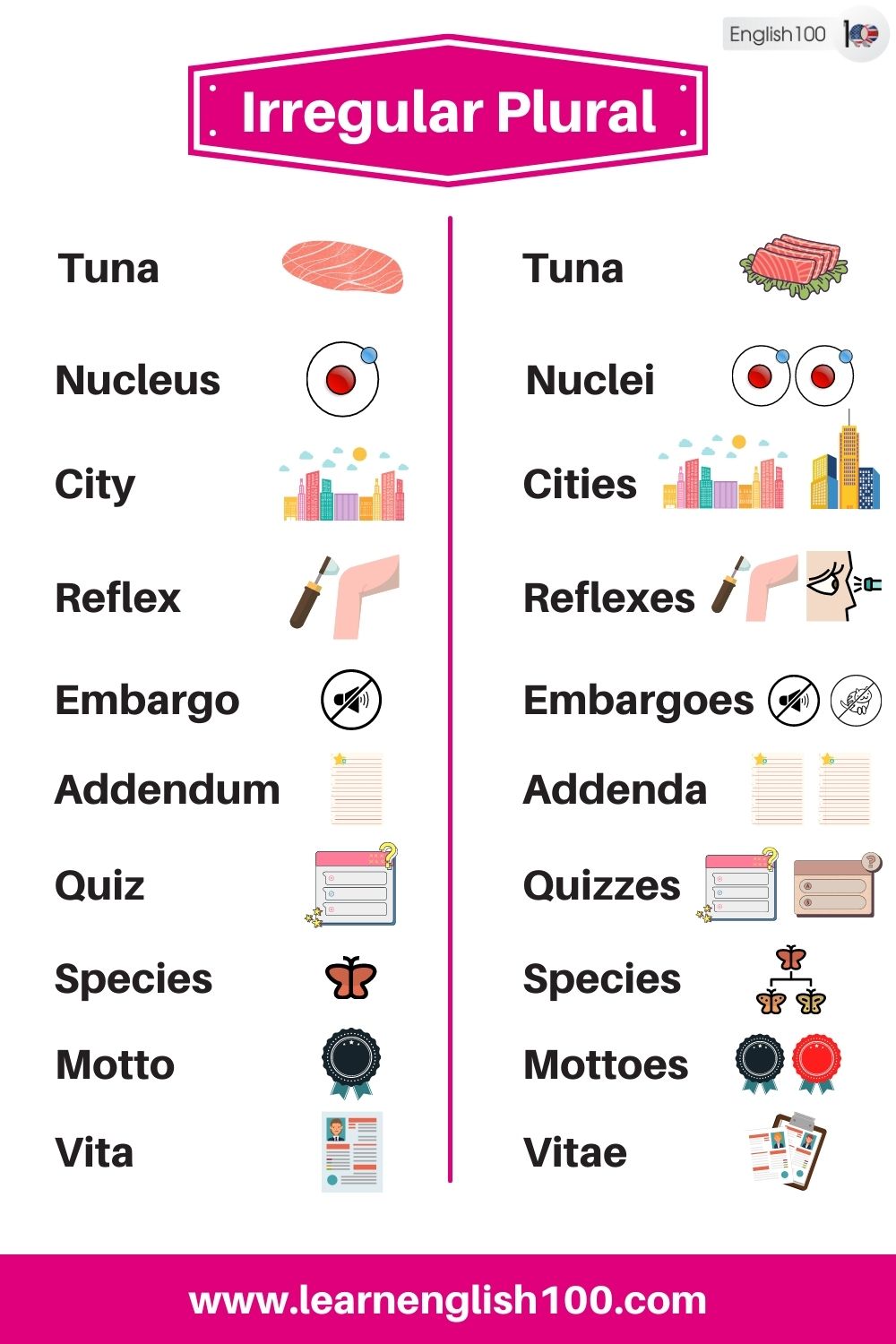
Tuna – Tuna
Nucleus – Nuclei
City – Cities
Reflex – Reflexes
Embargo – Embargoes
Addendum – Addenda
Quiz – Quizzes
Species – Species
Motto – Mottoes
Vita – Vitae
Barracks – Barracks
Potato – Potatoes
Kiss – Kisses
Apex – Apices
Try – Tries
Flush – Flushes
Church – Churches
Self – Selves
Bison – Bison
Hypothesis – Hypotheses
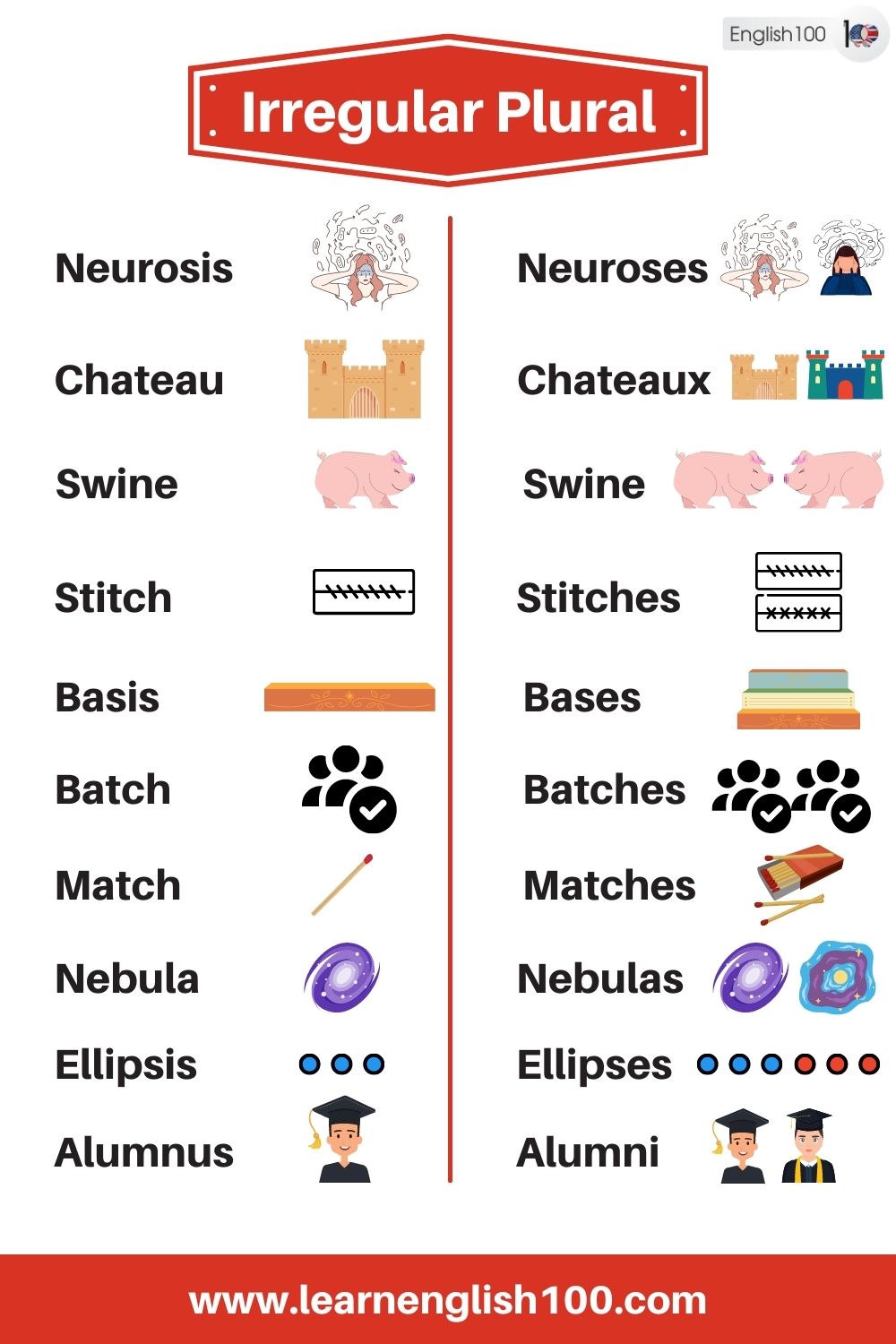
Neurosis – Neuroses
Chateau – Chateaux
Swine – Swine
Stitch – Stitches
Basis – Bases
Batch – Batches
Match – Matches
Potato – Potatoes
Nebula – Nebulae – Nebulas
Ellipsis – Ellipses
Alumnus – Alumni
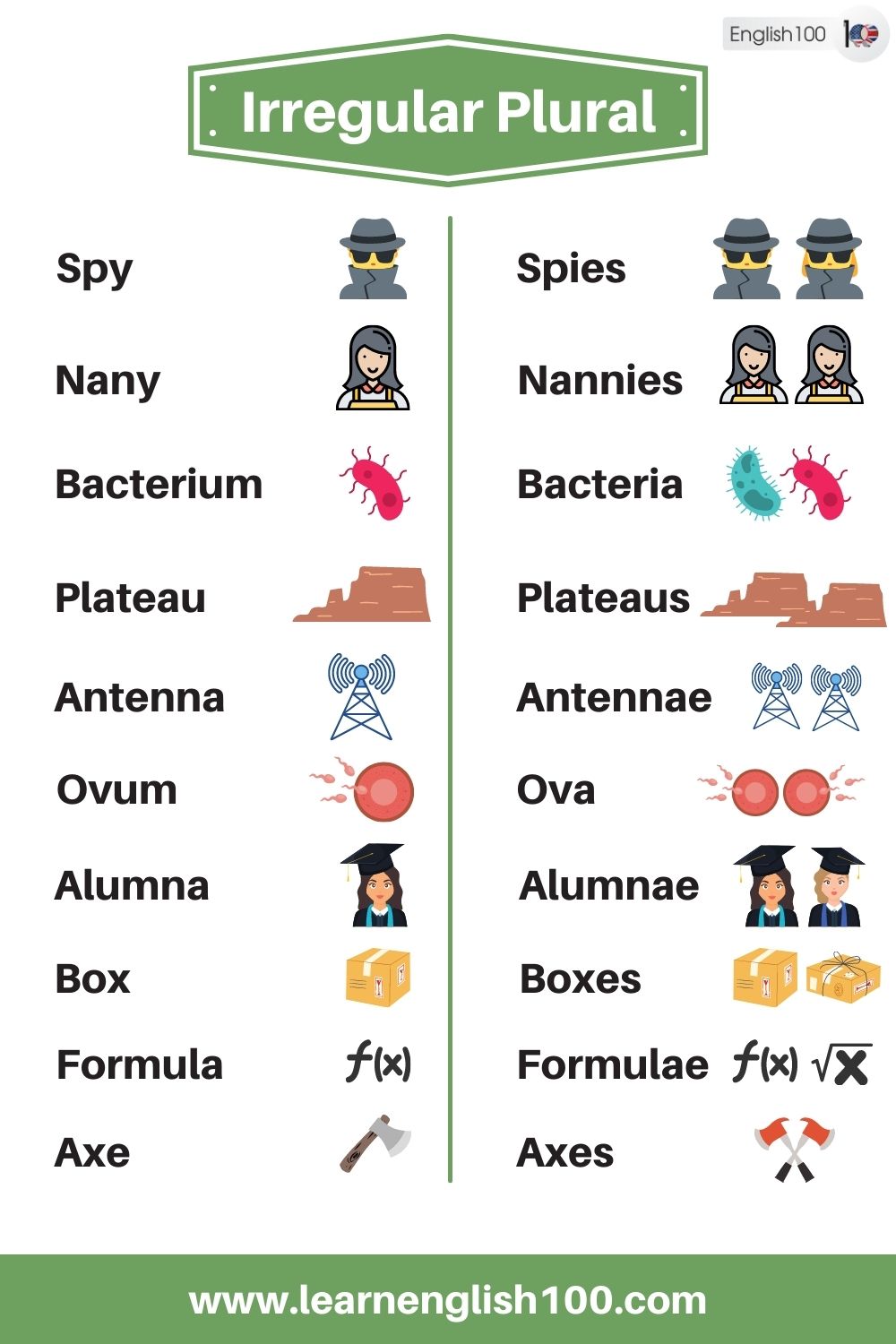
Spy – Spies
Nany – Nannies
Bacterium – Bacteria
Plateau – Plateaux – Plateaus
Antenna – Antennas – Antennae
Ovum – Ova
Alumna – Alumnae
Box – Boxes
Formula – Formulas – Formulae
Axe – Axes
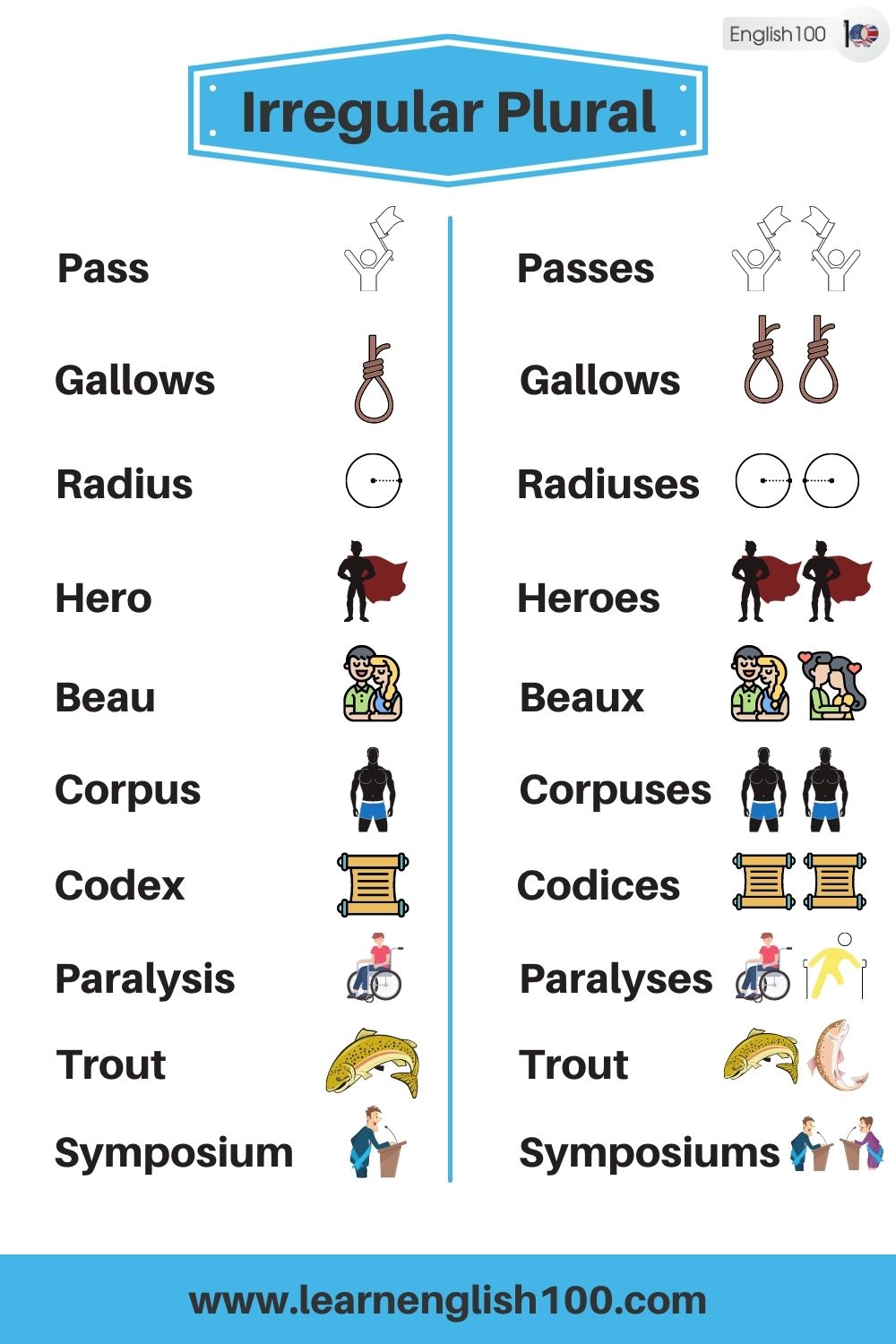
Pass – Passes
Gallows – Gallows
Radius – Radii – Radiuses
Hero – Heroes
Beau – Beaux
Corpus – Corpora – Corpuses
Codex – Codices
Paralysis – Paralyses
Trout – Trout
Symposium – Symposia – Symposiums
Circus – Circuses
Spacecraft – Spacecraft
Bus – Buses
Genus – Genera – Genuses
Penny – Pennies
Salmon – Salmon
Lady – Ladies
Phenomenon – Phenomena
Poppy – Poppies
Cod – Cod – Cods
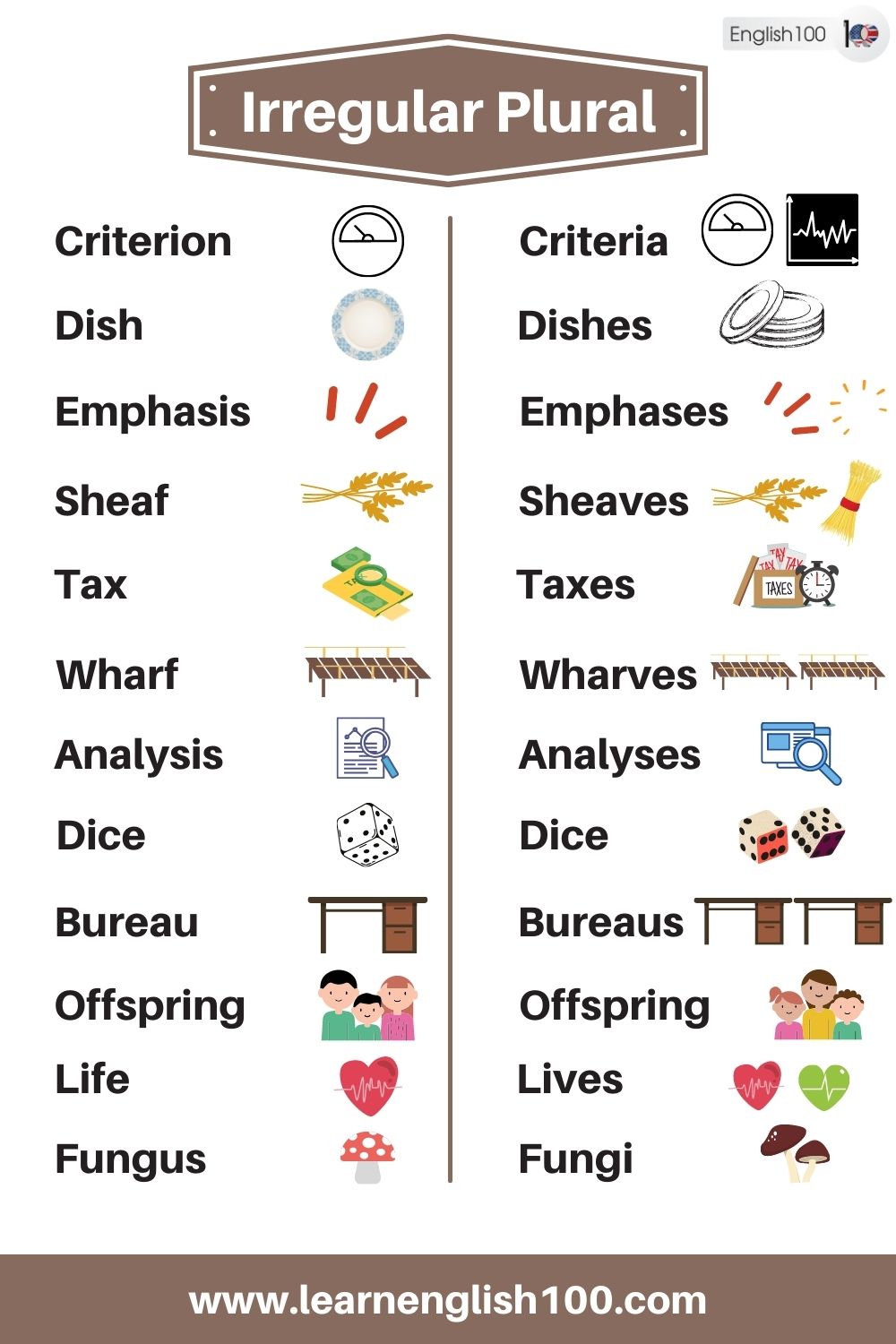
Criterion – Criteria
Dish – Dishes
Emphasis – Emphases
Sheaf – Sheaves
Tax – Taxes
Wharf – Wharves
Analysis – Analyses
Die – Dice
Bureau – Bureaux – Bureaus
Offspring – Offspring
Life – Lives
Fungus – Fungi
The basics of irregular plural nouns
As natives or new learners of the English language, we all know that in order to construct the plural form of a noun we usually add the letter “s” to the end of the word. However, we have to resort to adding “es” in certain cases where the specified noun ends in any of the following: ” S, Sh, X, Z, O, Ch”. But not all nouns that end with the vowel “O” need es to make the plural, you have to check the dictionary to make sure which one to use.
Other than the situation with the words that end with “O”, the case is very simple in regard to making the regular plurals for nouns. The irregular nouns on the other hand need to be memorized individually.
Pay attention to the words that already end in e like matrice which becomes matrices. In this case, we do not have to add an e and the “e “is not due to the plural form.
The word scissors have no singular form in the English language as well.
Note that there are words from Greek, Latin, or French origins that form the plural in a different manner, but it has a kind of a fixed rule in this area.
Also, note that certain words have more than one plural form and one of whom may be regular and the other is irregular. Furthermore, some words possess two irregular plural forms, and both with different endings.
It is important to remember that not all words that end in “f” are changed into “ves”. For example, the words roof and cliff are pluralized as follows roofs and cliffs without changing the letter f into “ves”.
Some words have regularly a different ending. For instance, the words that end with “um” usually end with an “a” at the end replacing the “um” part. The words that end in “is” in the singular when pluralized the “is” changes into an “es”.
Also, the “f” or “fe” at the end of a singular noun always changes into a “ves”. Words that end in a like larva, formula, and vita, its final “a” changes into “ae” in the plural form, larvae, formulae, vitae. The “y” at the end of the singular words has to be changed into and ie when pluralized. The “ex” ending words, like index, change the ex into ices when pluralized.
Irregular plurals, unlike regular plurals, don’t necessarily follow any particular pattern—instead, they follow a lot of different patterns. Because of this, irregular plurals require a lot of memorization; you need to remember which nouns belong to which type of pluralization. 1
FAQ about irregular plural nouns
What are irregular plural nouns examples?
Here are some examples of irregular plurals in English:
Man (singular) – Men (plural) Example: “The man is friendly. The men are friendly.”
Woman (singular) – Women (plural) Example: “She is a strong woman. They are strong women.”
Child (singular) – Children (plural) Example: “The child is playing. The children are playing.”
Foot (singular) – Feet (plural) Example: “He hurt his foot. They hurt their feet.”
Tooth (singular) – Teeth (plural) Example: “The tooth is loose. Her teeth are healthy.”
Goose (singular) – Geese (plural) Example: “The goose is swimming. The geese are swimming.”
Mouse (singular) – Mice (plural) Example: “The mouse is small. The mice are small.”
Person (singular) – People (plural) Example: “She’s a lovely person. They are friendly people.”
Die (singular) – Dice (plural) Example: “Roll the die. Roll the dice.”
Deer (singular and plural) Example: “The deer is graceful. The deer are graceful.”
Sheep (singular and plural) Example: “The sheep is grazing. The sheep are grazing.”
Fish (singular and plural in some contexts) Example: “The fish is colorful. The fish are colorful.”
What irregular plural nouns don’t change?
Some irregular plural nouns do not change in spelling between their singular and plural forms. These nouns have the same word for both singular and plural, which means they maintain their original form regardless of whether they refer to one or more than one entity. Here are some examples of irregular plural nouns that do not change:
Deer: “The deer is graceful. The deer are graceful.” In both the singular and plural forms, the word remains “deer.”
Sheep: “The sheep is grazing. The sheep are grazing.” Like “deer,” “sheep” remains the same for both singular and plural.
Fish: “The fish is colorful. The fish are colorful.” While “fish” can be used for both singular and plural, in some contexts, “fishes” is also used when referring to multiple species of fish.
Trout: “The trout is delicious. The trout are delicious.” “Trout” retains the same form for both singular and plural.
Salmon: “The salmon is flavorful. The salmon are flavorful.” Similar to “trout,” “salmon” does not change when used in plural form.
Species: “This species is endangered. These species are endangered.” “Species” remains the same in both singular and plural, with the context indicating the number.
Swine: “Swine flu is contagious. The swine flu outbreaks are concerning.” “Swine” is the same in both singular and plural forms.
To conclude, while irregular plural nouns may present a challenge to learners of English, they add depth and nuance to the language. Understanding them and using them correctly will enhance your language skills and help you communicate more effectively. Embrace the quirks of irregular plurals as part of the colorful tapestry of English language usage. You may like to read collective noun examples.
References:
